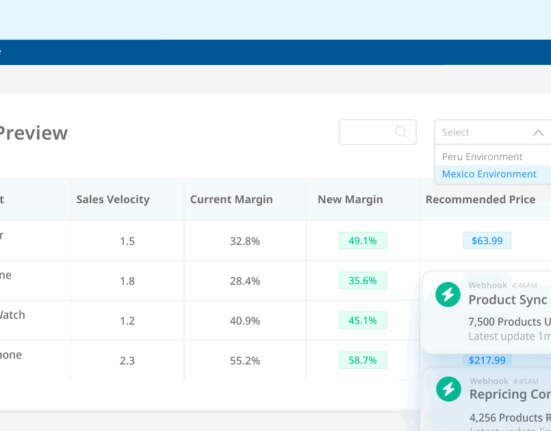
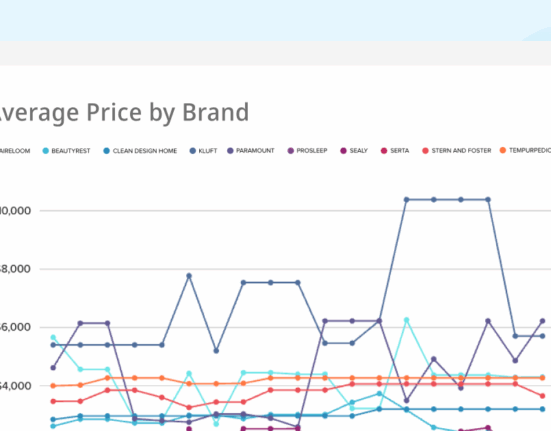
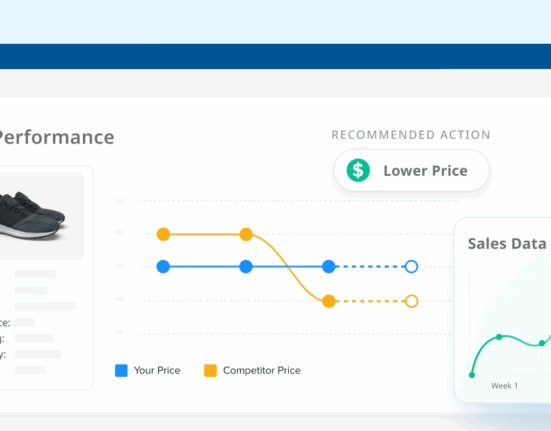
Understanding your product’s position in the market is crucial for success, especially when it comes to price. But what exactly is price positioning, and how does it impact a product’s success in the marketplace?
Price positioning refers to the process of determining where a product or service fits in relation to other offerings in the market, based on its price. It’s about strategically selecting a price point that communicates a certain value to consumers, thereby influencing their perception of the product or service.
In the battle for market share, price positioning can be a powerful tool. If done correctly, it can help brands differentiate themselves, attract the right target audience, and ultimately drive sales.
But What Is Price Positioning?
Price positioning is a marketing strategy that involves setting the price for a product or service in a way that appeals to a specific market segment. This approach takes into account the perceived value of the product or service to the customer, as well as how it compares to similar offerings from competitors. The goal is to position the product or service in such a way that it appears to provide the best value for the price, thus making it an attractive choice for the target market segment.
How price positioning is used can vary greatly depending on the industry, the product or service in question, and the specific market segment being targeted. For example, a luxury brand might use a high price positioning to convey the exclusivity and high quality of its products. On the other hand, a discount retailer might use a low price positioning to attract budget-conscious consumers looking for the best deal.

Regardless of the specific strategy used, the key to successful price positioning is ensuring that the price reflects the perceived value of the product or service to the target market. This involves understanding the market, the competition, and the customer’s needs and expectations. When done effectively, price positioning can help a company to attract its target market, differentiate its offerings from those of its competitors, and ultimately, drive sales and profitability.
Types of Price Positioning
Price positioning is a crucial aspect of a product’s marketing and pricing strategy, which significantly influences how the product is perceived in the marketplace. There are primarily three types of price positioning:
- Premium Pricing: This is when a product is priced higher than its competitors. Companies use premium pricing when they have a unique product or high brand value, and they want to position their product as high-quality or luxury.
- Competitive Pricing: With competitive pricing, products are priced similarly to competitors. This strategy is often used when the product features are similar to other products in the market, and companies want to compete directly on price.
- Economy Pricing: This strategy involves pricing a product lower than the competition. Companies utilize economy pricing to attract price-conscious customers and to position their product as an affordable option in the market. This is often used by companies that can maintain low production costs to sustain profitability at lower price points.
Factors Influencing Price Positioning
Th price positioning of a product or service can be influenced by a variety of factors. Such as:
Consumer Perception
The perception of a product’s value by consumers greatly influences its price positioning. If a product or brand is perceived as high quality, unique, or having a prestigious brand image, consumers may be willing to pay a higher price.
Conversely, if a product is viewed as undifferentiated or of lower quality, its pricing should be lower to attract potential buyers. The customer’s perception is often shaped by marketing efforts, brand reputation, and personal customer experience.
By understanding the intricate relationship between price and consumer behavior, businesses can strategically position their products to maximize sales and profitability.
Competitor Pricing
Price positioning is also significantly impacted by the pricing strategies of competing brands or products. Businesses often analyze the pricing of competitors’ offerings to identify a suitable range for their own products.
If the competition is priced lower, a company may need to justify a higher price with unique features or superior quality. On the other hand, if a product has similar features and quality to competitors but is priced higher, it may struggle to attract customers.
It’s important to closely monitor competitor pricing strategies and market responses to them to ensure optimal price positioning for your product.
Market Conditions
The current state of the market is another crucial factor that can influence price positioning.
In a market with high demand and low supply, prices can be positioned higher as consumers are more willing to pay. Conversely, in a market with low demand and high supply, prices may need to be lowered to attract customers.
Market trends, economic conditions, and consumer purchasing power also play a significant role in shaping price positioning strategies. During economic downturns, consumers often seek out lower-priced options, necessitating adjustments in price positioning.
Product Lifecycle
The lifecycle stage of a product can heavily influence its price positioning.
In the introduction phase, a company might set a higher price to recoup research and development costs, especially if the product is innovative with few competitors. During the growth phase, prices may remain stable or decline slightly as competition increases. In the maturity phase, prices generally decrease as competition intensifies and the market becomes saturated.
Finally, in the decline phase, companies might significantly reduce prices to clear out remaining inventory.

The Impact of Price Positioning on Consumer Behavior
Price positioning plays a significant role in influencing consumer behavior. It can be used as a strategic tool to shape consumers’ perception of a product or service, thereby affecting their purchasing decisions. This phenomenon, often referred to as the “price-quality heuristic,” is a common bias in consumer decision-making processes.
However, it’s essential to note that this isn’t always the case. Depending on the market and product type, some consumers may seek out lower-priced options, viewing them as more cost-effective or offering better value for money. For instance, in highly competitive markets with little differentiation between various products or services, consumers might be more price-sensitive and lean toward more competitively priced options.
Price positioning also impacts brand image and reputation. Both pricing higher and lower can be successful, but they attract different types of consumers and create divergent brand images.
The key takeaway is that price positioning isn’t a one-size-fits-all strategy. Businesses need to consider their target audience, product offerings, market competition, and overall brand image when deciding on their price positioning strategy. By understanding the intricate relationship between price and consumer behavior, businesses can strategically position their products to maximize sales and profitability.